The construction and manufacturing industries are cornerstones of modern economies, heavily reliant on materials that provide both strength and durability. One such essential material is Hot Rolled Plate, which is crucial for a variety of applications ranging from structural frameworks to heavy machinery. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global hot rolled plate market is projected to reach USD 220 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand from these sectors. This statistic underscores the importance of Hot Rolled Plate as a foundational element in industrial development.
Experts in the field agree on the pivotal role of Hot Rolled Plate. John Anderson, a leading metallurgical engineer at Steel Solutions Inc., states, "The versatility and durability of Hot Rolled Plate make it indispensable for the construction and manufacturing industries. It offers the mechanical properties that are essential for high-performance applications." His insights reflect the critical need for materials that not only meet engineering specifications but also contribute to the overall sustainability of projects in an increasingly competitive market.
As the industry evolves, the importance of Hot Rolled Plate will only continue to grow, signifying its status as a vital component in achieving robust infrastructure and innovative manufacturing solutions. Its application across diverse sectors amplifies its relevance, making it a key player in the future of construction and manufacturing.
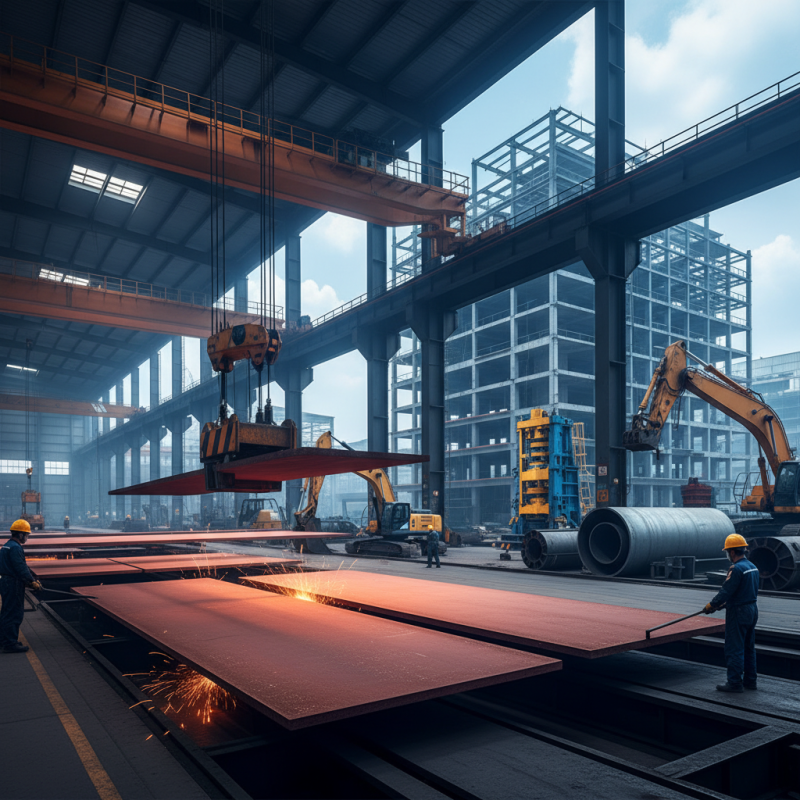

Hot rolled plate is a fundamental material in the construction and manufacturing industries, known for its distinct properties that make it suitable for a variety of applications. It is created through the process of rolling steel at high temperatures, which typically exceeds 1700°F (926°C). This high-temperature process allows for easier shaping and forming of the metal, resulting in a product that retains its structural integrity even when processed further. The mechanical properties of hot rolled plate include excellent ductility and toughness, which contribute to its widespread use in structural applications.
When considering the utilization of hot rolled plates, it is essential to understand their yield strength and tensile properties. According to the American Institute of Steel Construction, typical yield strengths for hot rolled structural steel plates can range from 36,000 psi to 58,000 psi, depending on the grade. This range makes hot rolled plates suitable for a variety of construction projects, including beams, columns, and flooring systems. The plates are also known for their weldability, allowing for easy integration into complex structures.
**Tips:** When selecting hot rolled plate for your next project, always check for certifications such as ASTM or ISO standards, which ensure the material meets specific quality requirements. Furthermore, consider the thickness of the plate, as this may affect your design choices and overall project budget. Additionally, using hot rolled plates sourced from reputable suppliers can help guarantee material consistency, ultimately leading to a more successful construction outcome.
| Property | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Can range from 3 mm to over 100 mm | Structural components in buildings and bridges |
| Strength | Excellent tensile and yield strength | Heavy machinery, industrial fabrication |
| Surface Finish | Rough surface due to hot rolling process | Welding and further processing |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Generally lower cost compared to cold rolled plate | Large-scale manufacturing and construction |
| Formability | Easily shaped, cut, or formed | Custom structures and components |
The manufacturing process of hot rolled plate involves several critical steps that transform raw materials into a vital component used in construction and manufacturing industries. Initially, large steel slabs or billets are heated in a furnace to a temperature above their recrystallization point, typically around 1,000°C. This high-temperature heating allows the steel to become malleable and easier to shape, facilitating the subsequent rolling process.
Once the steel reaches the desired temperature, it is passed through a series of rollers that apply immense pressure to form the plate. This process not only reduces the thickness of the steel but also enhances its mechanical properties. Post-rolling, the hot rolled plates are often cooled, either naturally or through controlled methods, which ensure that the final product retains its strength and toughness. The resulting plates exhibit uniform thickness and surface finishes, making them suitable for various applications in construction, automotive, and machinery sectors.
Additionally, the hot rolling process allows for significant flexibility in customizing plate dimensions and properties, leading to a wide range of product specifications. This adaptability, combined with the efficiency of hot rolling, makes it an essential technique in modern manufacturing, addressing the diverse needs of industries relying on robust and reliable materials.

Hot rolled plate, known for its versatility and strength, plays a crucial role in the construction industry. It is widely utilized in the fabrication of structural components such as beams, columns, and trusses. The primary advantage of hot rolling is that it allows for the production of plates in various thicknesses and sizes, accommodating the specific requirements of different construction projects. Whether it’s for building bridges or skyscrapers, hot rolled plates provide the necessary durability and structural integrity to support heavy loads and withstand various environmental conditions.
In addition to structural applications, hot rolled plates are often used in the manufacture of heavy equipment and machinery. They serve as the foundation for many elements of construction technology, from scaffolding to heavy-duty vehicles. Due to their inherent strength and resistance to deformation, these plates are ideal for applications that require high-stress resistance. Furthermore, the efficient manufacturing process of hot rolled plates makes them a cost-effective choice, allowing builders and manufacturers alike to meet both budgetary constraints and quality standards in their projects.
Hot rolled plate and cold rolled plate are two fundamental materials widely used in the construction and manufacturing industries, each possessing distinct characteristics that cater to specific applications.
Hot rolled plates are produced at high temperatures, typically above 1,700°F, which allows the metal to be easily shaped and formed. This process results in a thinner, more malleable sheet, making hot rolled plates ideal for structural applications where strength and durability are crucial.
According to industry statistics from the World Steel Association, hot rolled steel accounts for approximately 60% of total steel production, underscoring its significance in various structural applications.
In contrast, cold rolled plates undergo a process where metal is rolled at room temperature. This method enhances the surface finish and dimensional accuracy but can lead to increased brittleness and reduced ductility.
Cold rolled plates are primarily utilized in applications where precision and aesthetic appeal are paramount, such as automotive components and appliance manufacturing.
A report by the American Iron and Steel Institute highlights that cold rolled steel is preferred for manufacturing over 30% of metal products due to its fine surface quality and tighter tolerances.
Understanding these key differences in production methods and material properties can help industries make informed decisions about which type of plate best suits their operational needs.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for hot rolled plates is expected to witness significant growth driven by technological advancements and changing production methodologies. The application of hot rolled plates in sectors such as construction and manufacturing not only ensures structural integrity but also supports innovations in design and material efficiency. The ability to produce large plates with consistent quality while reducing costs will likely position hot rolled plates as a go-to material for future projects, especially in urban infrastructure and high-rise constructions.
Moreover, the sustainability trend is influencing the production and usage of hot rolled plates. Companies are increasingly focusing on eco-friendly practices, which include recycling and using greener production methods. As awareness of environmental impact grows, industries will seek hot rolled plates that are manufactured with minimal carbon footprints. This shift not only enhances the overall performance of machinery and structures but also aligns with global efforts toward sustainable development. Consequently, the future of hot rolled plates is intertwined with advances in manufacturing technology and the need for sustainable practices, indicating a promising trajectory for their use in various industries.