Choosing the right size and material for round pipes is crucial in construction and manufacturing. Reports indicate that improper sizing can cause 30% more material waste. Selecting suitable materials influences durability and cost-effectiveness. For instance, stainless steel round pipes are known for their corrosion resistance, making them ideal for industries like food processing.
Moreover, the average lifespan of round pipes varies significantly by material. PVC pipes, while cheaper, generally last about 25 years, whereas galvanized steel can last over 50. This disparity highlights the importance of informed decisions.
As you navigate this complex process, consider your project's specific requirements. The ideal choice isn't always clear-cut. Ensuring compatibility with existing systems is vital. Each project carries its unique challenges, and hasty decisions can lead to costly oversights. Reflecting on past experiences can guide you toward improving judgment in selecting round pipes.
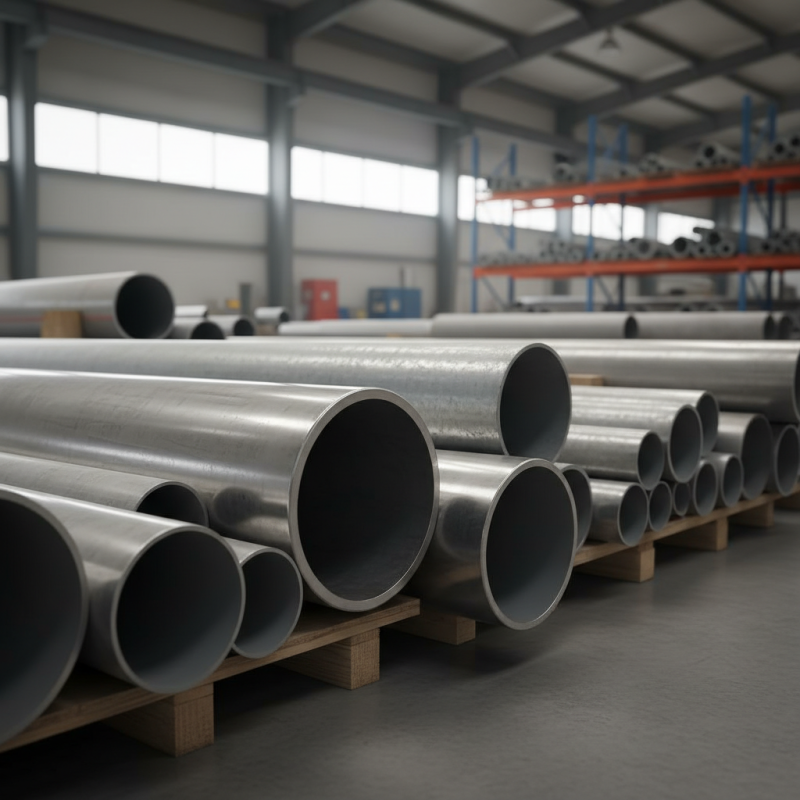

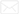
When choosing the right round pipe, understanding standard sizes is essential. Round pipes come in various diameters and wall thicknesses. The nominal size often differs from the actual size. Knowing how to convert measurements helps avoid confusion. For instance, a 2-inch pipe may have an outer diameter of 2.375 inches.
Standardization varies by region. In the U.S., you might encounter A106 or A53 specifications. Other countries have different systems. This variation can be tricky. Measurement mistakes can lead to project delays. It's crucial to double-check measurements before purchasing.
Tips for selecting the right size include measuring twice before buying. Consider the required pressure rating and environment. For example, high temperatures need specific materials. Always account for future modifications. Flexibility in size choices is beneficial. Test your choices on smaller projects. Be mindful; sometimes, opting for a slightly larger or smaller size proves more effective.
When choosing round pipes, material selection is crucial. Steel, PVC, and other options each come with distinct benefits and drawbacks. Steel pipes are strong and durable. They withstand high-pressure applications effectively. According to industry reports, steel pipes can last over 50 years in the right conditions. However, they are prone to corrosion. Proper coatings may be required, increasing overall maintenance costs.
PVC pipes are lightweight and resistant to corrosion. They are often used in residential plumbing and drainage applications. A report from the Plastic Pipe Institute highlights that PVC is more affordable upfront. Yet, its temperature tolerance is limited, which can lead to brittleness in colder climates. In some regions, it may not hold up against high-pressure water.
Aluminum and copper are other choices. Aluminum pipes are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They may not be as strong as steel but provide flexibility in design. Copper, while excellent for transferring heat and resistive to corrosion, is often more expensive. Each material has specific applications and considerations. Assessing the environment and purpose is key. Evaluate the installation costs and longevity potential for the best choice.
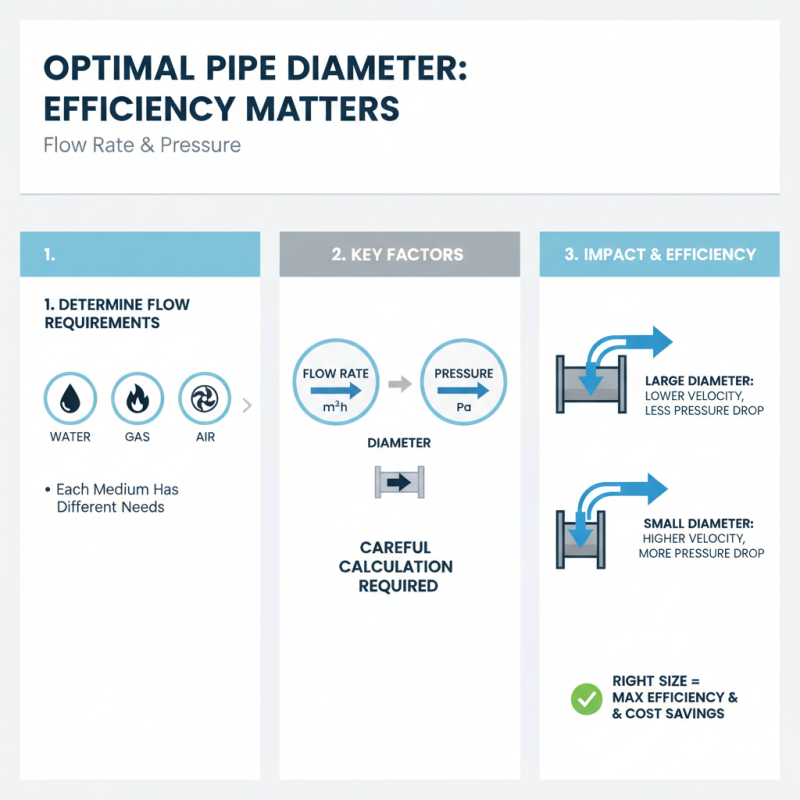
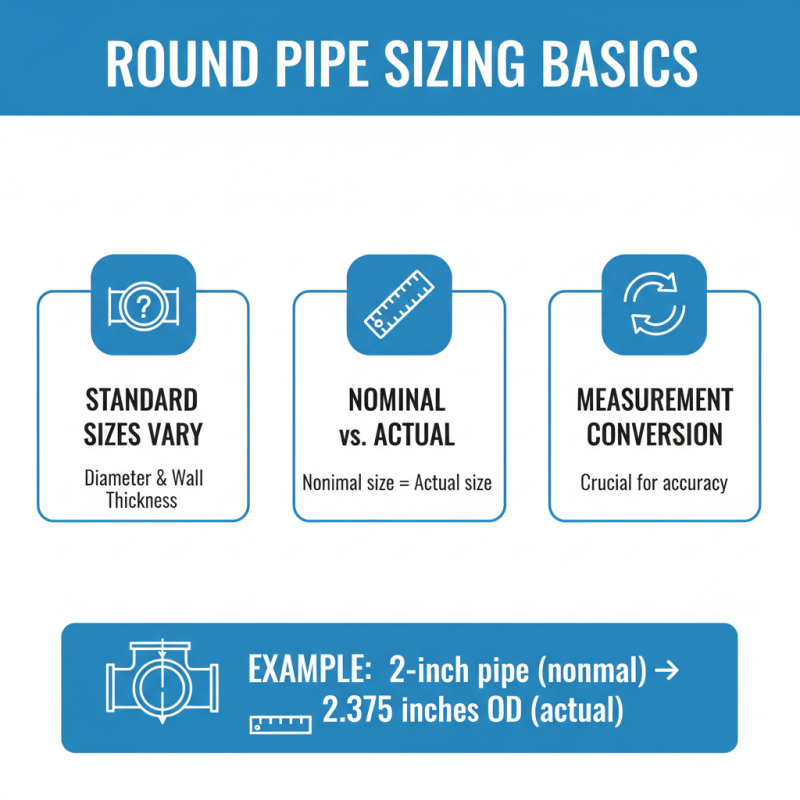
Choosing the right pipe diameter is crucial for efficiency. It impacts flow rate and pressure. For most applications, the diameter needs careful calculation. Begin by determining the flow requirements. Is it for water, gas, or air? Each has different needs.
Consider the system's length and layout. Longer pipes may require larger diameters. Narrow pipes can restrict flow and cause pressure drops. You might think a smaller size saves money. However, this can lead to problems. It's a common oversight.
Measurement methods vary. Using the right tools ensures accurate readings. Sometimes errors occur, leading to significant consequences. Pay attention to the material as well. Different substances handle pressure differently. Ensure compatibility with the application. Reflecting on these aspects can help avert costly mistakes.
Selecting the right round pipe material heavily depends on environmental conditions. Factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals play a crucial role. For instance, stainless steel may resist rusting, but it can fail in extreme acidic environments. This demonstrates the necessity of understanding specific use cases.
Galvanized steel is often chosen for outdoor use due to its weather resistance. However, it might corrode if exposed to salty conditions. PVC pipes, on the other hand, are lightweight and easy to install. Yet, they can become brittle in extreme temperatures. Analyzing these conditions helps in making informed choices.
Careful consideration of each factor is vital. A mismatch can lead to failures, affecting efficiency. Misjudging the environmental impact can result in costly repairs. Experience shows that a thorough evaluation of the environment pays off. It can prevent future headaches and improve longevity.
| Application | Material | Diameter (inches) | Thickness (mm) | Environmental Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Supply | PVC | 2 | 3 | Low pressure, non-corrosive |
| Gas Transportation | Steel | 4 | 5 | High pressure, outdoor use |
| Heating Systems | Copper | 1.5 | 2 | High temperature, low corrosiveness |
| Construction | Aluminum | 3 | 4 | Mild weather, structural uses |
| Chemical Handling | HDPE | 6 | 10 | Corrosive, underground use |
Choosing the right size and material for round pipes is crucial for optimal flow efficiency in various applications. Industry studies suggest that improper sizing can lead to significant energy losses. For example, a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers found that a 10% increase in pipe diameter can enhance flow capacity by up to 25%, but only if the material is selected appropriately.
Material choice also plays a key role. Stainless steel, while resistant to corrosion, may not always be the most economical option. In contrast, PVC provides a lighter and often less expensive alternative, but it lacks the durability needed for high-temperature applications. A study conducted by the Pipe Flow Management Group noted that up to 30% of flow inefficiencies stem from the wrong material, causing unnecessary operational costs.
Many professionals overlook the impact of fittings and valves, which can limit flow if not considered during the sizing process. Imperfect installation strategies can lead to leaks and pressure drops. Hence, attention to detail is essential while designing a system. Understanding these dimensions can greatly affect both efficiency and sustainability in fluid transport systems.