Cold Rolled Sheet is a versatile material used across various industries. Its production involves rolling steel at room temperature, which creates a smoother finish and tighter tolerances. This process enhances the mechanical properties of the steel, making it suitable for different applications.
In the automotive sector, Cold Rolled Sheet is crucial for manufacturing body panels and frames. The smooth surface allows for excellent paint adhesion. Additionally, appliances rely on Cold Rolled Sheet for components like washing machine frames. These items require durability and an appealing finish, which the material provides effectively.
However, challenges exist. Cold Rolled Sheet can be prone to corrosion if not properly coated. Industries need to ensure protective finishes are applied. There’s also the risk of surface defects, which could affect product quality. Users must be aware of these factors when choosing Cold Rolled Sheet for their projects.

Cold rolled sheets are widely utilized materials in various industries. These sheets are made through a process where steel is rolled at room temperature. This method gives them a unique set of properties. They are smoother, stronger, and more precise in thickness compared to hot rolled sheets.
One of the main characteristics of cold rolled sheets is their excellent surface finish. This quality allows for better paint adhesion and aesthetic appeal. They are ideal for applications in automotive manufacturing, appliances, and furniture. However, one must consider that the strength of cold rolled sheets can sometimes create challenges in forming and shaping. Certain designs may require additional considerations to prevent material failure.
Another notable feature is their high tensile strength. This strength makes them a preferred choice for construction and structural applications. However, this can lead to a heavier final product in some cases, which may not always be suitable for lightweight projects. Achieving a perfect balance in thickness and weight is often a point of reflection for engineers and designers. Understanding these properties helps users make informed decisions.
Cold rolled sheets are widely employed across various industries due to their strength and versatility. The automotive sector is one of the largest users. Cold rolled steel provides high tensile strength, ideal for auto body parts and internal structures. According to industry estimates, around 60% of cold rolled sheets are utilized in automotive manufacturing. The smooth finish allows for effective painting and coating, enhancing aesthetics and durability.
Another significant industry is construction. Cold rolled sheets form essential components in frames, support structures, and HVAC systems. The construction sector accounts for nearly 25% of global cold rolled sheet consumption. Their precision and thinner gauges can lead to cost savings. However, some challenges remain. For instance, improper handling can lead to surface defects, requiring additional finishing processes.
Electronics also benefit from cold rolled sheets, primarily in producing appliances and devices. Reports indicate that this sector has seen a steady increase in demand, with a projected growth rate of 5% over the next few years. Companies must pay attention to quality control in production to avoid unnecessary waste. Each of these industries highlights the broad application and importance of cold rolled sheets while recognizing areas for improvement.

Cold rolled sheets are widely used in various manufacturing sectors due to their versatility. One key application is in automotive production. These sheets are formed into body panels, helping create vehicles that are lightweight yet strong. The precise dimensions of cold rolled sheets allow for efficient assembly, yet they often need surface treatments to enhance durability and aesthetics.
Another important use is in the construction industry. Here, cold rolled sheets serve as essential components for structural support. Builders rely on these materials for framing and roofing systems. The smooth finish of cold rolled sheets often reveals imperfections that could affect the final product. Such flaws require careful inspection and quality control to prevent issues down the line.
In electronics, cold rolled sheets are utilized for casings and components. The precision of these sheets protects sensitive equipment from external damage. However, manufacturers must remain vigilant about the thickness and flatness of the sheets. Even slight deviations can lead to product failures. This area highlights the critical balance between efficiency and quality in production.
Cold rolled sheets are essential in construction and design. Their smooth surface offers superior aesthetics. This quality makes them ideal for visible structures. They are also lightweight, enhancing design flexibility. Yet, weaknesses do exist. They can be prone to corrosion if not protected properly.
When used correctly, cold rolled sheets provide excellent strength. The manufacturing process ensures tighter tolerances, resulting in precise dimensions. This is crucial in construction projects. Accurate measurements lead to better assembly. Errors can cause delays and increased costs.
Tips for using cold rolled sheets include proper coating. A good finish prevents rusting. Always check for defects during procurement. Small flaws can compromise structural integrity. Additionally, consider the design requirements carefully. Evaluate whether cold rolled sheets meet your project needs before proceeding.
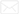
This chart illustrates the various applications of cold rolled sheets across different industries. The data presents the percentage of usage in automotive, construction, electrical appliances, furniture, and machinery sectors, highlighting the versatility and advantages of cold rolled sheets in modern manufacturing and construction.
Cold rolled sheets and hot rolled sheets serve distinct purposes in various industries. Cold rolled sheets are known for their superior surface finish and tighter tolerances. They are ideal for applications where precision is key. These sheets are commonly used in automotive parts and appliance components. Their smooth surface allows for excellent paint adhesion and aesthetic appeal.
Hot rolled sheets, on the other hand, are typically used in structural applications. Their rough surface and lower cost make them suitable for construction projects. However, the dimensional accuracy is not as high as cold rolled sheets. For example, you wouldn't use hot rolled sheets for intricate designs. While both have their merits, it's important to consider specific project needs.
Tips: Always inspect the thickness and flatness of sheets before use. This can save time and ensure quality. Consider the environmental impact of the manufacturing process. Sometimes, cold rolled sheets may not be the sustainable choice. Evaluate the long-term effects on your projects and choose wisely.
| Application | Material Type | Advantages | Typical Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Parts | Cold Rolled Steel | High strength, excellent surface finish | 0.7 - 3.0 mm |
| Furniture | Cold Rolled Steel | Smooth edges, aesthetic appeal | 0.5 - 2.5 mm |
| Electrical Appliances | Cold Rolled Steel | Durability, electrical insulation capability | 0.4 - 2.0 mm |
| Construction | Cold Rolled Steel | High precision, better formability | 1.0 - 4.0 mm |
| Machinery Components | Cold Rolled Steel | Enhanced surface smoothness, reduced oxidation | 0.6 - 3.5 mm |
| Type | Characteristics | Common Uses | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Rolled | Smooth surface, precise dimensions | Car bodies, furniture, appliances | Higher |
| Hot Rolled | Rough surface, less precise | Construction beams, rail tracks | Lower |